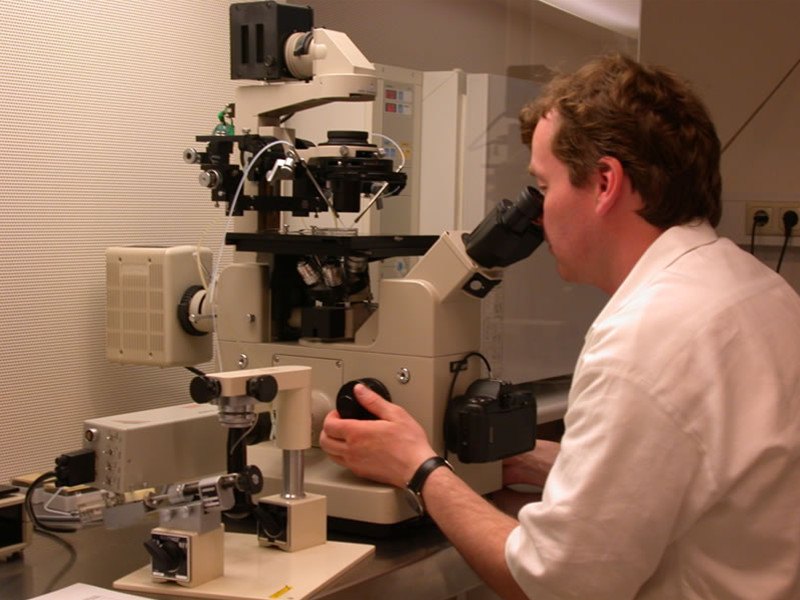
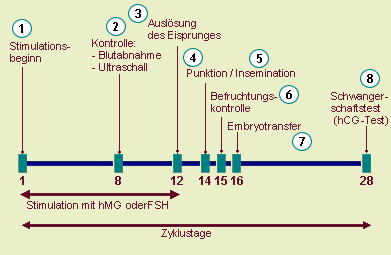
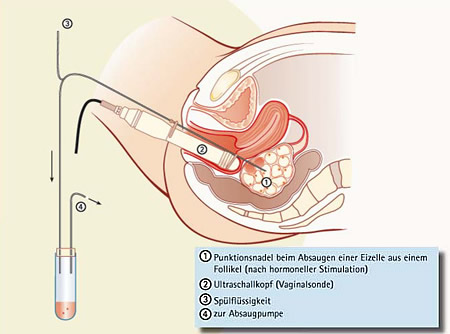
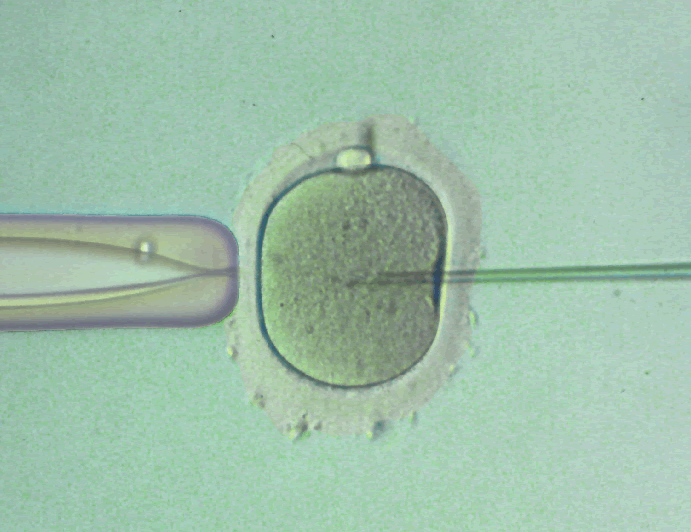
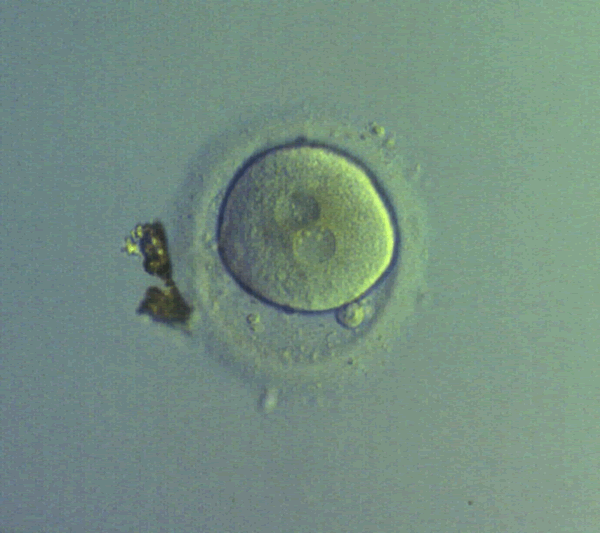
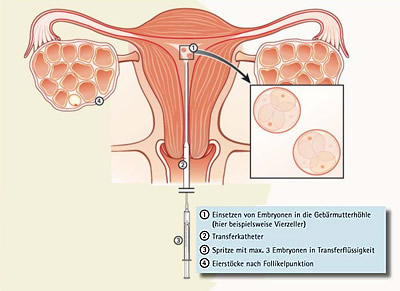
The fertility treatment consists of three consecutive steps:
- hormonal stimulation of the woman
- gaining of egg cells, fertilization of egg cells, embryo transfer
- waiting period until the pregnancy test
We perform two variants of hormonal stimulation to adjust it to each individual woman. Dependent on the method the fertility treatment takes between 4 and 10 weeks.